Cellulose diacetate
Appearance
This article needs additional citations for verification. (June 2012) |
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| ChemSpider |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
| variable | |
| Molar mass | variable |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
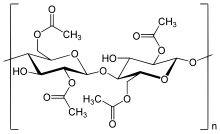
Cellulose diacetate, sometimes called diacetate, is a
functional groups on each unit of D-anhydroglucopyranose of the cellulose molecule. It was first developed in the United States
.
It is fragile since it is based on cellulose. When cellulose diacetate deteriorates, it shrinks and releases acetic acid causing vinegar syndrome.
Cellulose diacetate has been used to make fabrics, membranes, filaments, and many consumer products. From 1922 to 1957 it was used to make
In photography, a film substrate made from cellulose diacetate is called safety film.
Cellulose diacetate is
biodegradable.[3]
See also
References
- ^ Friuli, M., Nitti, P., Cafuero, L. et al. Cellulose Acetate and Cardanol Based Seed Coating for Intraspecific Weeding Coupled with Natural Herbicide Spraying. J Polym Environ (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-020-01821-9
- ISSN 0888-5885.
- ISSN 2328-8930.
