Hydrogen
 Purple glow in its plasma state | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Colorless gas | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight Ar°(H) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen in the periodic table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
kJ/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | (H2) 0.904 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar heat capacity | (H2) 28.836 J/(mol·K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vapor pressure
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Discovery | Henry Cavendish[7][8] (1766) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Named by | Louis-Bernard Guyton de Morveau Antoine Lavoisier[9][10] (1787) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isotopes of hydrogen | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Hydrogen is a
In the early universe, the formation of hydrogen's protons occurred during the first second following the
Historically, hydrogen gas was first produced artificially in the early 16th century through the reaction of acids with metals. Henry Cavendish, between 1766 and 1781, identified hydrogen gas as a distinct substance[16] and discovered its property of producing water when burned—hence its name derived from the Greek "water-former".
Today, the majority of
Properties
Combustion
Hydrogen gas is highly flammable:
- 2 H2(g) + O2(g) → 2 H2O(l) (572 kJ/2 mol = 286 kJ/mol = 141.865 MJ/kg)[note 2]
The
Hydrogen gas forms explosive mixtures with air in concentrations from 4–74%[22] and with chlorine at 5–95%. The hydrogen autoignition temperature, the temperature of spontaneous ignition in air, is 500 °C (932 °F).[23]
Flame
Pure
Reactants
H2 is unreactive compared to diatomic elements such as
Electron energy levels

The ground state energy level of the electron in a hydrogen atom is −13.6 eV,[28] which is equivalent to an ultraviolet photon of roughly 91 nm wavelength.[29]
The energy levels of hydrogen can be calculated fairly accurately using the
A more accurate description of the hydrogen atom comes from a purely quantum mechanical treatment that uses the Schrödinger equation, Dirac equation or Feynman path integral formulation to calculate the probability density of the electron around the proton.[31] The most complicated treatments allow for the small effects of special relativity and vacuum polarization. In the quantum mechanical treatment, the electron in a ground state hydrogen atom has no angular momentum at all—illustrating how the "planetary orbit" differs from electron motion.
Spin isomers
Molecular H2 exists as two spin isomers, i.e. compounds that differ only in the spin states of their nuclei.[32] In the orthohydrogen form, the spins of the two nuclei are parallel, forming a spin triplet state having a total molecular spin ; in the parahydrogen form the spins are antiparallel and form a spin singlet state having spin . The equilibrium ratio of ortho- to para-hydrogen depends on temperature. At room temperature or warmer, equilibrium hydrogen gas contains about 25% of the para form and 75% of the ortho form.[33] The ortho form is an excited state, having higher energy than the para form by 1.455 kJ/mol,[34] and it converts to the para form over the course of several minutes when cooled to low temperature.[35] The thermal properties of the forms differ because they differ in their allowed rotational quantum states, resulting in different thermal properties such as the heat capacity.[36]
The ortho-to-para ratio in H2 is an important consideration in the
Phases


- Gaseous hydrogen
- Liquid hydrogen
- Slush hydrogen
- Solid hydrogen
- Metallic hydrogen
- Plasma hydrogen
Compounds
Covalent and organic compounds
While H2 is not very reactive under standard conditions, it does form compounds with most elements. Hydrogen can form compounds with elements that are more
Hydrogen forms a vast array of compounds with
Hydrogen is highly soluble in many
Hydrides

Compounds of hydrogen are often called
Although hydrides can be formed with almost all main-group elements, the number and combination of possible compounds varies widely; for example, more than 100 binary borane hydrides are known, but only one binary aluminium hydride.[51] Binary indium hydride has not yet been identified, although larger complexes exist.[52]
In
Protons and acids
Oxidation of hydrogen removes its electron and gives H+, which contains no electrons and a nucleus which is usually composed of one proton. That is why H+ is often called a proton. This species is central to discussion of acids. Under the Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, acids are proton donors, while bases are proton acceptors.
A bare proton, H+, cannot exist in solution or in ionic crystals because of its unstoppable attraction to other atoms or molecules with electrons. Except at the high temperatures associated with plasmas, such protons cannot be removed from the
To avoid the implication of the naked "solvated proton" in solution, acidic aqueous solutions are sometimes considered to contain a less unlikely fictitious species, termed the "hydronium ion" ([H3O]+). However, even in this case, such solvated hydrogen cations are more realistically conceived as being organized into clusters that form species closer to [H9O4]+.[54] Other oxonium ions are found when water is in acidic solution with other solvents.[55]
Although exotic on Earth, one of the most common ions in the universe is the H+3 ion, known as protonated molecular hydrogen or the trihydrogen cation.[56]
Isotopes



Hydrogen has three naturally occurring isotopes, denoted 1
H, 2
H and 3
H. Other, highly unstable nuclei (4
H to 7
H) have been synthesized in the laboratory but not observed in nature.[57][58]
- 1
H is the most common hydrogen isotope, with an abundance of more than 99.98%. Because the nucleus of this isotope consists of only a single proton, it is given the descriptive but rarely used formal name protium.[59] It is unique among all stable isotopes in having no neutrons; see diproton for a discussion of why others do not exist. - 2
H, the other stable hydrogen isotope, is known asNMR spectroscopy.[60] Heavy water is used as a neutron moderator and coolant for nuclear reactors. Deuterium is also a potential fuel for commercial nuclear fusion.[61] - 3
H is known asradiolabel.[67]
Unique among the elements, distinct names are assigned to its isotopes in common use today. During the early study of radioactivity, various heavy radioactive isotopes were given their own names, but such names are no longer used, except for deuterium and tritium. The symbols D and T (instead of 2
H and 3
H) are sometimes used for deuterium and tritium, but the symbol P is already in use for
H, and 3
H to be used, although 2
H and 3
H are preferred.[69]
The exotic atom muonium (symbol Mu), composed of an antimuon and an electron, can also be considered a light radioisotope of hydrogen.[70] Because muons decay with lifetime 2.2 µs, muonium is too unstable to exhibit observable chemistry.[71] Nevertheless, muonium compounds are important test cases for quantum simulation, due to the mass difference between the antimuon and the proton,[72] and IUPAC nomenclature incorporates such hypothetical compounds as muonium chloride (MuCl) and sodium muonide (NaMu), analogous to hydrogen chloride and sodium hydride respectively.[73]
Thermal and physical properties
Table of thermal and physical properties of hydrogen (H2) at atmospheric pressure:[74][75]
| Temperature (K) | Density (kg/m^3) | Specific heat (kJ/kg K) | Dynamic viscosity (kg/m s) | Kinematic viscosity (m^2/s) | Thermal conductivity (W/m K) | Thermal diffusivity (m^2/s) | Prandtl Number |
| 100 | 0.24255 | 11.23 | 4.21E-06 | 1.74E-05 | 6.70E-02 | 2.46E-05 | 0.707 |
| 150 | 0.16371 | 12.602 | 5.60E-06 | 3.42E-05 | 0.0981 | 4.75E-05 | 0.718 |
| 200 | 0.1227 | 13.54 | 6.81E-06 | 5.55E-05 | 0.1282 | 7.72E-05 | 0.719 |
| 250 | 0.09819 | 14.059 | 7.92E-06 | 8.06E-05 | 0.1561 | 1.13E-04 | 0.713 |
| 300 | 0.08185 | 14.314 | 8.96E-06 | 1.10E-04 | 0.182 | 1.55E-04 | 0.706 |
| 350 | 0.07016 | 14.436 | 9.95E-06 | 1.42E-04 | 0.206 | 2.03E-04 | 0.697 |
| 400 | 0.06135 | 14.491 | 1.09E-05 | 1.77E-04 | 0.228 | 2.57E-04 | 0.69 |
| 450 | 0.05462 | 14.499 | 1.18E-05 | 2.16E-04 | 0.251 | 3.16E-04 | 0.682 |
| 500 | 0.04918 | 14.507 | 1.26E-05 | 2.57E-04 | 0.272 | 3.82E-04 | 0.675 |
| 550 | 0.04469 | 14.532 | 1.35E-05 | 3.02E-04 | 0.292 | 4.52E-04 | 0.668 |
| 600 | 0.04085 | 14.537 | 1.43E-05 | 3.50E-04 | 0.315 | 5.31E-04 | 0.664 |
| 700 | 0.03492 | 14.574 | 1.59E-05 | 4.55E-04 | 0.351 | 6.90E-04 | 0.659 |
| 800 | 0.0306 | 14.675 | 1.74E-05 | 5.69E-04 | 0.384 | 8.56E-04 | 0.664 |
| 900 | 0.02723 | 14.821 | 1.88E-05 | 6.90E-04 | 0.412 | 1.02E-03 | 0.676 |
| 1000 | 0.02424 | 14.99 | 2.01E-05 | 8.30E-04 | 0.448 | 1.23E-03 | 0.673 |
| 1100 | 0.02204 | 15.17 | 2.13E-05 | 9.66E-04 | 0.488 | 1.46E-03 | 0.662 |
| 1200 | 0.0202 | 15.37 | 2.26E-05 | 1.12E-03 | 0.528 | 1.70E-03 | 0.659 |
| 1300 | 0.01865 | 15.59 | 2.39E-05 | 1.28E-03 | 0.568 | 1.96E-03 | 0.655 |
| 1400 | 0.01732 | 15.81 | 2.51E-05 | 1.45E-03 | 0.61 | 2.23E-03 | 0.65 |
| 1500 | 0.01616 | 16.02 | 2.63E-05 | 1.63E-03 | 0.655 | 2.53E-03 | 0.643 |
| 1600 | 0.0152 | 16.28 | 2.74E-05 | 1.80E-03 | 0.697 | 2.82E-03 | 0.639 |
| 1700 | 0.0143 | 16.58 | 2.85E-05 | 1.99E-03 | 0.742 | 3.13E-03 | 0.637 |
| 1800 | 0.0135 | 16.96 | 2.96E-05 | 2.19E-03 | 0.786 | 3.44E-03 | 0.639 |
| 1900 | 0.0128 | 17.49 | 3.07E-05 | 2.40E-03 | 0.835 | 3.73E-03 | 0.643 |
| 2000 | 0.0121 | 18.25 | 3.18E-05 | 2.63E-03 | 0.878 | 3.98E-03 | 0.661 |
History
Discovery and use
Robert Boyle

In 1671, the Irish scientist Robert Boyle discovered and described the reaction between iron filings and dilute acids, which results in the production of hydrogen gas.[76][77]
Having provided a saline spirit [hydrochloric acid], which by an uncommon way of preparation was made exceeding sharp and piercing, we put into a vial, capable of containing three or four ounces of water, a convenient quantity of filings of steel, which were not such as are commonly sold in shops to Chymists and Apothecaries, (those being usually not free enough from rust) but such as I had a while before caus'd to be purposely fil'd off from a piece of good steel. This metalline powder being moistn'd in the viol with a little of the menstruum, was afterwards drench'd with more; whereupon the mixture grew very hot, and belch'd up copious and stinking fumes; which whether they consisted altogether of the volatile sulfur of the Mars [iron], or of metalline steams participating of a sulfureous nature, and join'd with the saline exhalations of the menstruum, is not necessary to be here discuss'd. But whencesoever this stinking smoak proceeded, so inflammable it was, that upon the approach of a lighted candle to it, it would readily enough take fire, and burn with a blewish and somewhat greenish flame at the mouth of the viol for a good while together; and that, though with little light, yet with more strength than one would easily suspect.
— Robert Boyle, Tracts written by the Honourable Robert Boyle containing new experiments, touching the relation betwixt flame and air...
The word "sulfureous" may be somewhat confusing, especially since Boyle did a similar experiment with iron and sulfuric acid.[78] However, in all likelihood, "sulfureous" should here be understood to mean combustible.[79]
Henry Cavendish
In 1766,
Antoine Lavoisier

In 1783, Antoine Lavoisier identified the element that came to be known as hydrogen[82] when he and Laplace reproduced Cavendish's finding that water is produced when hydrogen is burned.[8] Lavoisier produced hydrogen for his experiments on mass conservation by reacting a flux of steam with metallic iron through an incandescent iron tube heated in a fire. Anaerobic oxidation of iron by the protons of water at high temperature can be schematically represented by the set of following reactions:
- 1) Fe + H2O → FeO + H2
- 2) Fe + 3 H2O → Fe2O3 + 3 H2
- 3) Fe + 4 H2O → Fe3O4 + 4 H2
Many metals such as zirconium undergo a similar reaction with water leading to the production of hydrogen.
19th century
François Isaac de Rivaz built the first de Rivaz engine, an internal combustion engine powered by a mixture of hydrogen and oxygen in 1806. Edward Daniel Clarke invented the hydrogen gas blowpipe in 1819. The Döbereiner's lamp and limelight were invented in 1823.[8]
Hydrogen was liquefied for the first time by James Dewar in 1898 by using regenerative cooling and his invention, the vacuum flask.[8] He produced solid hydrogen the next year.[8]
Hydrogen-lifted airship

The first hydrogen-filled balloon was invented by Jacques Charles in 1783.[8] Hydrogen provided the lift for the first reliable form of air-travel following the 1852 invention of the first hydrogen-lifted airship by Henri Giffard.[8] German count Ferdinand von Zeppelin promoted the idea of rigid airships lifted by hydrogen that later were called Zeppelins; the first of which had its maiden flight in 1900.[8] Regularly scheduled flights started in 1910 and by the outbreak of World War I in August 1914, they had carried 35,000 passengers without a serious incident. Hydrogen-lifted airships were used as observation platforms and bombers during the war.
The first non-stop transatlantic crossing was made by the British airship
Deuterium and tritium
Deuterium was discovered in December 1931 by Harold Urey, and tritium was prepared in 1934 by Ernest Rutherford, Mark Oliphant, and Paul Harteck.[7] Heavy water, which consists of deuterium in the place of regular hydrogen, was discovered by Urey's group in 1932.[8]
Hydrogen-cooled turbogenerator
The first
Nickel–hydrogen battery
The nickel–hydrogen battery was used for the first time in 1977 aboard the U.S. Navy's Navigation technology satellite-2 (NTS-2).[84] The International Space Station,[85] Mars Odyssey[86] and the Mars Global Surveyor[87] are equipped with nickel-hydrogen batteries. In the dark part of its orbit, the Hubble Space Telescope is also powered by nickel-hydrogen batteries, which were finally replaced in May 2009,[88] more than 19 years after launch and 13 years beyond their design life.[89]
Role in quantum theory

Because of its simple atomic structure, consisting only of a proton and an electron, the
One of the first quantum effects to be explicitly noticed (but not understood at the time) was a Maxwell observation involving hydrogen, half a century before full
Antihydrogen (
H
) is the antimatter counterpart to hydrogen. It consists of an antiproton with a positron. Antihydrogen is the only type of antimatter atom to have been produced as of 2015[update].[92][93]
Cosmic prevalence and distribution

Hydrogen, as atomic H, is the most abundant chemical element in the universe, making up 75 percent of normal matter by mass and more than 90 percent by number of atoms. (Most of the mass of the universe, however, is not in the form of chemical-element type matter, but rather is postulated to occur as yet-undetected forms of mass such as dark matter and dark energy.[94])
Hydrogen is found in great abundance in stars and
States
Throughout the universe, hydrogen is mostly found in the
Hydrogen is found in the neutral atomic state in the interstellar medium because the atoms seldom collide and combine. They are the source of the 21-cm hydrogen line at 1420 MHz that is detected in order to probe primordial hydrogen.[96] The large amount of neutral hydrogen found in the damped Lyman-alpha systems is thought to dominate the cosmological baryonic density of the universe up to a redshift of z = 4.[97]
Under ordinary conditions on Earth, elemental hydrogen exists as the diatomic gas, H2. Hydrogen gas is very rare in the Earth's atmosphere (around 0.53
A molecular form called
Production
Many methods exist for producing H2, but three dominate commercially: steam reforming often coupled to water-gas shift, partial oxidation of hydrocarbons, and water electrolysis.[102]
Steam reforming
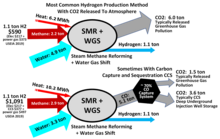
Hydrogen is mainly produced by steam methane reforming (SMR), the reaction of water and methane.[103][104] [105] Thus, at high temperatures (1000–1400 K, 700–1100 °C or 1300–2000 °F), steam (water vapor) reacts with methane to yield carbon monoxide and H2.
- CH4 + H2O → CO + 3 H2
Steam reforming is also used for the industrial preparation of ammonia.
This reaction is favored at low pressures, Nonetheless, conducted at high pressures (2.0 MPa, 20 atm or 600
- CH4 → C + 2 H2
Consequently, steam reforming typically employs an excess of H2O. Additional hydrogen can be recovered from the steam by use of carbon monoxide through the
- CO + H2O → CO2 + H2
Hydrogen is sometimes produced and consumed in the same industrial process, without being separated. In the Haber process for the production of ammonia, hydrogen is generated from natural gas.[106]
Partial oxidation of hydrocarbons
Other methods for CO and H2 production include partial oxidation of hydrocarbons:[107]
- 2 CH4 + O2 → 2 CO + 4 H2
Although less important commercially, coal can serve as a prelude to the shift reaction above:[105]
- C + H2O → CO + H2
Olefin production units may produce substantial quantities of byproduct hydrogen particularly from cracking light feedstocks like ethane or propane.[108]
Water electrolysis

The electrolysis of water is a conceptually simple method of producing hydrogen.
- 2 H2O(l) → 2 H2(g) + O2(g)
Commercial
Electrolysis of brine to yield chlorine also produces hydrogen as a co-product.[110]
Methane pyrolysis
Hydrogen can be produced by pyrolysis of natural gas (methane).
This route has a lower carbon footprint than commercial hydrogen production processes.[111][112][113][114] Developing a commercial methane pyrolysis process could expedite the expanded use of hydrogen in industrial and transportation applications. Methane pyrolysis is accomplished by passing methane through a molten metal catalyst containing dissolved nickel. Methane is converted to hydrogen gas and solid carbon.[115][116]
- CH4(g) → C(s) + 2 H2(g) (ΔH° = 74 kJ/mol)
The carbon may be sold as a manufacturing feedstock or fuel, or landfilled.
Further research continues in several laboratories, including at Karlsruhe Liquid-metal Laboratory [117] and at University of California – Santa Barbara.[118] BASF built a methane pyrolysis pilot plant.[119]
Thermochemical
More than 200 thermochemical cycles can be used for
Laboratory methods
H2 is produced in laboratories, often as a by-product of other reactions. Many metals react with water to produce H2, but the rate of hydrogen evolution depends on the metal, the pH, and the presence of alloying agents. Most commonly, hydrogen evolution is induced by acids. The alkali and alkaline earth metals, aluminium, zinc, manganese, and iron react readily with aqueous acids. This reaction is the basis of the Kipp's apparatus, which once was used as a laboratory gas source:
- Zn + 2 H+ → Zn2+ + H2
In the absence of acid, the evolution of H2 is slower. Because iron is widely used structural material, its anaerobic corrosion is of technological significance:
- Fe + 2 H2O → Fe(OH)2 + H2
Many metals, such as aluminium, are slow to react with water because they form passivated oxide coatings of oxides. An alloy of aluminium and gallium, however, does react with water.[122] At high pH, aluminium can produce H2:
- 2 Al + 6 H2O + 2 OH− → 2 [Al(OH)4]− + 3 H2
Some metal-containing compounds react with acids to evolve H2. Under anaerobic conditions,
2) can be oxidized by the protons of water to form magnetite and H2. This process is described by the Schikorr reaction
- 3 Fe(OH)2 → Fe3O4 + 2 H2O + H2
This process occurs during the anaerobic corrosion of iron and steel in oxygen-free groundwater and in reducing soils below the water table.
Biohydrogen
H2 is produced by hydrogenase enzymes in some fermentation.[123]
Wells
There is a well in Mali and deposits in several other countries, such as France.[124]
Applications

Petrochemical industry
Large quantities of H2 are used in the "upgrading" of
- R2S + 2 H2 → H2S + 2 RH
Hydrogenation
Coolant
Hydrogen is commonly used in power stations as a coolant in generators due to a number of favorable properties that are a direct result of its light diatomic molecules. These include low
Energy carrier
Elemental hydrogen is widely discussed in the context of energy as an energy carrier with potential to help the decarbonisation of economies and mitigate greenhouse gas emissions.[128][129] This therefore requires hydrogen to be produced cleanly in quantities to be supplied in sectors and applications where cheaper and more energy-efficient mitigation alternatives are limited. These include heavy industry and long-distance transport.[128] Hydrogen is a ''carrier'' of energy rather than an energy resource, because there is no naturally occurring source of hydrogen in useful quantities.[130]
Hydrogen can be deployed as an energy source in
Electricity can be used to split water molecules, producing sustainable hydrogen, provided the electricity was generated sustainably. However, this electrolysis process is currently more expensive than creating hydrogen from methane without CCS and the efficiency of energy conversion is inherently low.[129] Hydrogen can be produced when there is a surplus of variable renewable electricity, then stored and used to generate heat or to re-generate electricity.[135] Hydrogen created through electrolysis using renewable energy is commonly referred to as "green hydrogen."[136] It can be further transformed into synthetic fuels such as ammonia and methanol.[137]
Innovation in hydrogen electrolysers could make large-scale production of hydrogen from electricity more cost-competitive.[138] There is potential for hydrogen produced this way to play a significant role in decarbonising energy systems where there are challenges and limitations to replacing fossil fuels with direct use of electricity.[128]
Hydrogen fuel can produce the intense heat required for industrial production of steel, cement, glass, and chemicals, thus contributing to the decarbonisation of industry alongside other technologies, such as
Disadvantages of hydrogen as an energy carrier include high costs of storage and distribution due to hydrogen's explosivity, its large volume compared to other fuels, and its tendency to make pipes brittle.[134]
Semiconductor industry
Hydrogen is employed to saturate broken ("dangling") bonds of
Niche and evolving uses
- Shielding gas: Hydrogen is used as a shielding gas in welding methods such as atomic hydrogen welding.[147][148]
- Cryogenic research: Liquid H2 is used in cryogenic research, including superconductivity studies.[149]
- Buoyant lifting: Because H2 is lighter than air, having only 7% of the density of air, it was once widely used as a lifting gas in balloons and airships.[150]
- Leak detection: Pure or mixed with nitrogen (sometimes called tracer gas for detection of minute leaks. Applications can be found in the automotive, chemical, power generation, aerospace, and telecommunications industries.[151] Hydrogen is an authorized food additive (E 949) that allows food package leak testing, as well as having anti-oxidizing properties.[152]
- Neutron moderation: Deuterium (hydrogen-2) is used in nuclear fission applications as a moderator to slow neutrons.
- Nuclear fusion fuel: Deuterium is used in nuclear fusion reactions.[8]
- Isotopic labeling: Deuterium compounds have applications in chemistry and biology in studies of isotope effects on reaction rates.[153]
- Rocket propellant: Liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen together serve as cryogenic fuel in liquid-propellant rockets, as in the Space Shuttle main engines. NASA has investigated the use of rocket propellant made from atomic hydrogen, boron or carbon that is frozen into solid molecular hydrogen particles that are suspended in liquid helium. Upon warming, the mixture vaporizes to allow the atomic species to recombine, heating the mixture to high temperature.[154]
- Tritium uses: hydrogen bombs,[155] as an isotopic label in the biosciences,[67] and as a source of beta radiation in radioluminescent paint for instrument dials and emergency signage.[62]
Biological reactions
H2 is a product of some types of
Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the human body in terms of numbers of
Safety and precautions
| Hazards | |
|---|---|
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Danger | |
| H220 | |
| P202, P210, P271, P377, P381, P403[163] | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Hydrogen poses a number of hazards to human safety, from potential
Even interpreting the hydrogen data (including safety data) is confounded by a number of phenomena. Many physical and chemical properties of hydrogen depend on the parahydrogen/orthohydrogen ratio (it often takes days or weeks at a given temperature to reach the equilibrium ratio, for which the data is usually given). Hydrogen detonation parameters, such as critical detonation pressure and temperature, strongly depend on the container geometry.[164]
See also
- Combined cycle hydrogen power plant
- Hydrogen economy – Using hydrogen to decarbonize sectors which are hard to electrify
- Hydrogen production – Industrial production of molecular hydrogen
- Hydrogen safety – Procedures for safe production, handling and use of hydrogen
- Hydrogen technologies – Technologies that relating to the production & use of hydrogen
- Hydrogen transport
- Liquid hydrogen – Liquid state of the element hydrogen
- Methane pyrolysis– Thermal decomposition of materials (for hydrogen)
- Natural hydrogen – Molecular hydrogen naturally occurring on Earth
- Pyrolysis – Thermal decomposition of materials
Notes
- ^ However, most of the universe's mass is not in the form of baryons or chemical elements. See dark matter and dark energy.
- ^ 286 kJ/mol: energy per mole of the combustible material (molecular hydrogen).
References
- ^ "Standard Atomic Weights: Hydrogen". CIAAW. 2009.
- ISSN 1365-3075.
- ISBN 978-0123526519.
- ISBN 978-1-62708-155-9.
- ISBN 978-0-8493-0486-6.
- ISBN 978-0-8493-0464-4.
- ^ ISBN 978-0-471-61525-5.
- ^ ISBN 978-0-19-850341-5.
- .
- ISBN 978-0-19-508083-4.
- ^ "Dihydrogen". O=CHem Directory. University of Southern Maine. Archived from the original on 13 February 2009. Retrieved 6 April 2009.
- ^ "Hydrogen". Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 24 December 2021. Retrieved 25 December 2021.
- ^ Boyd, Padi (19 July 2014). "What is the chemical composition of stars?". NASA. Archived from the original on 15 January 2015. Retrieved 5 February 2008.
- doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.98.030001. Archived (PDF) from the original on 29 June 2021 – via Particle Data Group at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory..
Chapter 21.4.1 - This occurred when the age of the Universe was about 370,000 years.
(Revised September 2017) by Keith A. Olive and John A. Peacock - ^ Laursen, S.; Chang, J.; Medlin, W.; Gürmen, N.; Fogler, H. S. (27 July 2004). "An extremely brief introduction to computational quantum chemistry". Molecular Modeling in Chemical Engineering. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on 20 May 2015. Retrieved 4 May 2015.
- ^ Presenter: Professor Jim Al-Khalili (21 January 2010). "Discovering the Elements". Chemistry: A Volatile History. 25:40 minutes in. BBC. BBC Four. Archived from the original on 25 January 2010. Retrieved 9 February 2010.
- from the original on 15 February 2022. Retrieved 4 February 2022.
- ^ "Hydrogen Basics – Production". Florida Solar Energy Center. 2007. Archived from the original on 18 February 2008. Retrieved 5 February 2008.
- ^ license.
- ^ S2CID 19429952.
- ISBN 978-0-309-09163-3. Archivedfrom the original on 29 January 2021. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- .
- ISBN 978-0-471-71458-3. Archivedfrom the original on 26 January 2021. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- from the original on 29 January 2021. Retrieved 30 June 2019.
- ^ "Myths about the Hindenburg Crash". Airships.net. Archived from the original on 20 April 2021. Retrieved 29 March 2021.
- ISBN 0-8493-0487-3.
- ISBN 978-0-521-82381-4.
- ^ NAAP Labs (2009). "Energy Levels". University of Nebraska Lincoln. Archived from the original on 11 May 2015. Retrieved 20 May 2015.
- ^ "photon wavelength 13.6 eV". Wolfram Alpha. 20 May 2015. Archived from the original on 12 May 2016. Retrieved 20 May 2015.
- ^ Stern, D. P. (16 May 2005). "The Atomic Nucleus and Bohr's Early Model of the Atom". NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (mirror). Archived from the original on 17 October 2008. Retrieved 20 December 2007.
- ^ Stern, D. P. (13 February 2005). "Wave Mechanics". NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. Archived from the original on 13 May 2008. Retrieved 16 April 2008.
- ^ Staff (2003). "Hydrogen (H2) Properties, Uses, Applications: Hydrogen Gas and Liquid Hydrogen". Universal Industrial Gases, Inc. Archived from the original on 19 February 2008. Retrieved 5 February 2008.
- from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 28 August 2021.
- ^ "Die Entdeckung des para-Wasserstoffs (The discovery of para-hydrogen)". Max-Planck-Institut für Biophysikalische Chemie (in German). Archived from the original on 16 November 2020. Retrieved 9 November 2020.
- S2CID 120832814.
- ^ Hritz, J. (March 2006). "CH. 6 – Hydrogen" (PDF). NASA Glenn Research Center Glenn Safety Manual, Document GRC-MQSA.001. NASA. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 February 2008. Retrieved 5 February 2008.
- ^ Amos, Wade A. (1 November 1998). "Costs of Storing and Transporting Hydrogen" (PDF). National Renewable Energy Laboratory. pp. 6–9. Archived (PDF) from the original on 26 December 2014. Retrieved 19 May 2015.
- .
- ^ Clark, J. (2002). "The Acidity of the Hydrogen Halides". Chemguide. Archived from the original on 20 February 2008. Retrieved 9 March 2008.
- ^ Kimball, J. W. (7 August 2003). "Hydrogen". Kimball's Biology Pages. Archived from the original on 4 March 2008. Retrieved 4 March 2008.
- ^ IUPAC Compendium of Chemical Terminology, Electronic version, Hydrogen Bond Archived 19 March 2008 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Sandrock, G. (2 May 2002). "Metal-Hydrogen Systems". Sandia National Laboratories. Archived from the original on 24 February 2008. Retrieved 23 March 2008.
- ^ a b "Structure and Nomenclature of Hydrocarbons". Purdue University. Archived from the original on 11 June 2012. Retrieved 23 March 2008.
- ^ "Organic Chemistry". Dictionary.com. Lexico Publishing Group. 2008. Archived from the original on 18 April 2008. Retrieved 23 March 2008.
- ^ "Biochemistry". Dictionary.com. Lexico Publishing Group. 2008. Archived from the original on 29 March 2008. Retrieved 23 March 2008.
- .
- .
- .
- ^ Christensen, C. H.; Nørskov, J. K.; Johannessen, T. (9 July 2005). "Making society independent of fossil fuels – Danish researchers reveal new technology". Technical University of Denmark. Archived from the original on 21 May 2015. Retrieved 19 May 2015.
- (PDF) from the original on 24 August 2019. Retrieved 24 August 2019.
- .
- doi:10.1039/a809279f.
- ^ ISBN 978-0-13-035471-6.
- .
- .
- .
- S2CID 122902571.
- PMID 12633420.
- PMID 17797765.
- S2CID 28027551.
- ^ Broad, W. J. (11 November 1991). "Breakthrough in Nuclear Fusion Offers Hope for Power of Future". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 29 January 2021. Retrieved 12 February 2008.
- ^ a b Traub, R. J.; Jensen, J. A. (June 1995). "Tritium radioluminescent devices, Health and Safety Manual" (PDF). International Atomic Energy Agency. p. 2.4. Archived (PDF) from the original on 6 September 2015. Retrieved 20 May 2015.
- ^ Staff (15 November 2007). "Tritium". U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Archived from the original on 2 January 2008. Retrieved 12 February 2008.
- ^ Nave, C. R. (2006). "Deuterium-Tritium Fusion". HyperPhysics. Georgia State University. Archived from the original on 16 March 2008. Retrieved 8 March 2008.
- doi:10.1016/B978-0-444-81546-0.50009-4. Archived from the originalon 14 March 2008. Retrieved 8 March 2008.
- ^ "The Tritium Laboratory". University of Miami. 2008. Archived from the original on 28 February 2008. Retrieved 8 March 2008.
- ^ S2CID 13159020.
- ^ van der Krogt, P. (5 May 2005). "Hydrogen". Elementymology & Elements Multidict. Archived from the original on 23 January 2010. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
- ^ § IR-3.3.2, Provisional Recommendations Archived 9 February 2016 at the Wayback Machine, Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry, Chemical Nomenclature and Structure Representation Division, IUPAC. Accessed on line 3 October 2007.
- ISBN 978-0-86542-684-9. Archivedfrom the original on 13 March 2008. Retrieved 15 November 2016.
- .
- ISSN 0026-8976.
- (PDF) from the original on 14 May 2011. Retrieved 15 November 2016.
- OCLC 46959719.
- OCLC 62532755.
- ^ Boyle, R. (1672). Tracts written by the Honourable Robert Boyle containing new experiments, touching the relation betwixt flame and air, and about explosions, an hydrostatical discourse occasion'd by some objections of Dr. Henry More against some explications of new experiments made by the author of these tracts: To which is annex't, an hydrostatical letter, dilucidating an experiment about a way of weighing water in water, new experiments, of the positive or relative levity of bodies under water, of the air's spring on bodies under water, about the differing pressure of heavy solids and fluids. Printed for Richard Davis. pp. 64–65.
- ^ Winter, M. (2007). "Hydrogen: historical information". WebElements Ltd. Archived from the original on 10 April 2008. Retrieved 5 February 2008.
- S2CID 231776282.
- ^ Ramsay, W. (1896). The gases of the atmosphere: The history of their discovery. Macmillan. p. 19.
- ISBN 978-0-521-21110-9. Retrieved 22 October 2011.
- JSTOR 105491.
- ISBN 978-0-19-508083-4.
- ^ National Electrical Manufacturers Association (1946). A chronological history of electrical development from 600 B.C. New York, N.Y., National Electrical Manufacturers Association. p. 102. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 9 February 2016.
- doi:10.2514/3.57704.
- ISBN 0-7803-7296-4. Archived(PDF) from the original on 14 May 2010. Retrieved 11 November 2011.
- S2CID 108678345.
- ^ "Mars Global Surveyor". Astronautix.com. Archived from the original on 10 August 2009. Retrieved 6 April 2009.
- ^ Lori Tyahla, ed. (7 May 2009). "Hubble servicing mission 4 essentials". NASA. Archived from the original on 13 March 2015. Retrieved 19 May 2015.
- ^ Hendrix, Susan (25 November 2008). Lori Tyahla (ed.). "Extending Hubble's mission life with new batteries". NASA. Archived from the original on 5 March 2016. Retrieved 19 May 2015.
- ISBN 978-1-4298-0723-4.
- .
- S2CID 23581065.
- S2CID 58906869.
- ^ Gagnon, S. "Hydrogen". Jefferson Lab. Archived from the original on 10 April 2008. Retrieved 5 February 2008.
- ^ Haubold, H.; Mathai, A. M. (15 November 2007). "Solar Thermonuclear Energy Generation". Columbia University. Archived from the original on 11 December 2011. Retrieved 12 February 2008.
- ^ "Hydrogen". mysite.du.edu. Archived from the original on 18 April 2009. Retrieved 20 April 2008.
- S2CID 120150880.
- ^ PMID 36890228.
- Bibcode:2004APS..MAR.m1001D. Archived from the original(PDF) on 13 February 2008. Retrieved 5 February 2008.
- ^ McCall Group; Oka Group (22 April 2005). "H3+ Resource Center". Universities of Illinois and Chicago. Archived from the original on 11 October 2007. Retrieved 5 February 2008.
- ISBN 978-1-4613-4915-0
- ^ ISBN 9780471484943.
- ^ Freyermuth, George H. "1934 Patent: "The manufacture of hydrogen from methane hydrocarbons by the action of steam at elevated temperature"". Patent Full-Text Databases. United States Patent and Trademark Office. Archived from the original on 1 October 2021. Retrieved 30 October 2020.
- ISBN 978-0-471-77985-8.
- ^ ISBN 978-0-03-035373-4.
- ^ Funderburg, E. (2008). "Why Are Nitrogen Prices So High?". The Samuel Roberts Noble Foundation. Archived from the original on 9 May 2001. Retrieved 11 March 2008.
- ^ "Hydrogen Properties, Uses, Applications". Universal Industrial Gases, Inc. 2007. Archived from the original on 27 March 2008. Retrieved 11 March 2008.
- ISSN 0961-9534.
- S2CID 205329127.
- ^ Lees, A. (2007). "Chemicals from salt". BBC. Archived from the original on 26 October 2007. Retrieved 11 March 2008.
- from the original on 8 November 2020. Retrieved 31 October 2020.
- .
- ^ Cartwright, Jon. "The reaction that would give us clean fossil fuels forever". New Scientist. Archived from the original on 26 October 2020. Retrieved 30 October 2020.
- ^ Karlsruhe Institute of Technology. "Hydrogen from methane without CO2 emissions". Phys.Org. Archived from the original on 21 October 2020. Retrieved 30 October 2020.
- S2CID 206663568.
- from the original on 29 January 2021. Retrieved 31 October 2020.
- ^ Gusev, Alexander. "KITT/IASS – Producing CO2 Free Hydrogen From Natural Gas For Energy Usage". European Energy Innovation. Institute for Advanced Sustainability Studies. Archived from the original on 29 January 2021. Retrieved 30 October 2020.
- ^ Fernandez, Sonia. "Researchers develop potentially low-cost, low-emissions technology that can convert methane without forming CO2". Phys-Org. American Institute of Physics. Archived from the original on 19 October 2020. Retrieved 19 October 2020.
- ^ BASF. "BASF researchers working on fundamentally new, low-carbon production processes, Methane Pyrolysis". United States Sustainability. BASF. Archived from the original on 19 October 2020. Retrieved 19 October 2020.
- ^ Weimer, Al (25 May 2005). "Development of solar-powered thermochemical production of hydrogen from water" (PDF). Solar Thermochemical Hydrogen Generation Project. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 April 2007. Retrieved 21 December 2008.
- ^ Perret, R. "Development of Solar-Powered Thermochemical Production of Hydrogen from Water, DOE Hydrogen Program, 2007" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 May 2010. Retrieved 17 May 2008.
- .
- PMID 17845059.
- ^ "Natural Hydrogen: A Potential Clean Energy Source Beneath Our Feet". Yale E360. Retrieved 27 January 2024.
- ^ Barnard, Michael (22 October 2023). "What's New On The Rungs Of Liebreich's Hydrogen Ladder?". CleanTechnica. Retrieved 10 March 2024.
- ISBN 978-0-262-69313-4.
- ^ Chemistry Operations (15 December 2003). "Hydrogen". Los Alamos National Laboratory. Archived from the original on 4 March 2011. Retrieved 5 February 2008.
- ^ ISBN 9781009157926.
- ^ a b Evans, Simon; Gabbatiss, Josh (30 November 2020). "In-depth Q&A: Does the world need hydrogen to solve climate change?". Carbon Brief. Archived from the original on 1 December 2020. Retrieved 1 December 2020.
- ^ McCarthy, J. (31 December 1995). "Hydrogen". Stanford University. Archived from the original on 14 March 2008. Retrieved 14 March 2008.
- from the original on 14 July 2021. Retrieved 14 July 2021.
- ISBN 978-92-9260-151-5. Archived(PDF) from the original on 29 September 2021. Retrieved 17 October 2021..
- ^ Bonheure, Mike; Vandewalle, Laurien A.; Marin, Guy B.; Van Geem, Kevin M. (March 2021). "Dream or Reality? Electrification of the Chemical Process Industries". CEP Magazine. American Institute of Chemical Engineers. Archived from the original on 17 July 2021. Retrieved 6 July 2021.
- ^ from the original on 16 October 2021. Retrieved 11 September 2021.
- ISSN 0098-1354.
- ^ "Hydrogen industry must clean itself up before expanding into new…". Canary Media. 31 August 2021. Retrieved 5 April 2023.
- ISBN 978-92-9260-334-2. Archived(PDF) from the original on 11 June 2021.
- ^ IEA (2021). Net Zero by 2050: A Roadmap for the Global Energy Sector (PDF). pp. 15, 75–76. Archived (PDF) from the original on 23 May 2021.
- ^ Kjellberg-Motton, Brendan (7 February 2022). "Steel decarbonisation gathers speed | Argus Media". www.argusmedia.com. Retrieved 7 September 2023.
- Rocky Mountain Institute. pp. 2, 7, 8. Archived(PDF) from the original on 22 September 2020.
- S2CID 246465284.
- .
- (PDF) from the original on 15 August 2017. Retrieved 1 August 2018.
- PMID 17143265.
- S2CID 96415065.
- .
- .
- ^ "Atomic Hydrogen Welding". Specialty Welds. 2007. Archived from the original on 16 July 2011.
- .
- ISBN 978-0-306-47277-0. Retrieved 20 May 2015.
- ^ Block, M. (3 September 2004). Hydrogen as Tracer Gas for Leak Detection. 16th WCNDT 2004. Montreal, Canada: Sensistor Technologies. Archived from the original on 8 January 2009. Retrieved 25 March 2008.
- ^ "Report from the Commission on Dietary Food Additive Intake" (PDF). European Union. Archived (PDF) from the original on 16 February 2008. Retrieved 5 February 2008.
- PMID 7410413.
- ^ "NASA/TM—2002-211915: Solid Hydrogen Experiments for Atomic Propellants" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 July 2021. Retrieved 2 July 2021.
- from the original on 19 April 2008. Retrieved 13 April 2008.
- ISBN 978-0-415-24242-4. Archivedfrom the original on 29 January 2021. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- (PDF) from the original on 24 August 2019. Retrieved 24 August 2019.
- S2CID 257625443.
- S2CID 31706721. Archived from the original(PDF) on 29 January 2021. Retrieved 26 December 2020.
- (PDF) from the original on 29 January 2021. Retrieved 24 August 2019.
- ^ Smith, Hamilton O.; Xu, Qing (2005). "IV.E.6 Hydrogen from Water in a Novel Recombinant Oxygen-Tolerant Cyanobacteria System" (PDF). FY2005 Progress Report. United States Department of Energy. Archived (PDF) from the original on 29 December 2016. Retrieved 6 August 2016.
- ^ Williams, C. (24 February 2006). "Pond life: the future of energy". Science. The Register. Archived from the original on 9 May 2011. Retrieved 24 March 2008.
- ^ "MyChem: Chemical" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 October 2018. Retrieved 1 October 2018.
- ^ a b Brown, W. J.; et al. (1997). "Safety Standard for Hydrogen and Hydrogen Systems" (PDF). NASA. NSS 1740.16. Archived (PDF) from the original on 1 May 2017. Retrieved 12 July 2017.
- ^ "Liquid Hydrogen MSDS" (PDF). Praxair, Inc. September 2004. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 May 2008. Retrieved 16 April 2008.
- JSTOR 3970088.
- ^ Hayes, B. "Union Oil Amine Absorber Tower". TWI. Archived from the original on 20 November 2008. Retrieved 29 January 2010.
- ISBN 978-0-8247-2478-8. Retrieved 20 May 2015.
Further reading
- The Hyperfine Splitting in Hydrogen - The Feynman Lectures on Physics
- Chart of the Nuclides (17th ed.). Knolls Atomic Power Laboratory. 2010. ISBN 978-0-9843653-0-2.
- Newton, David E. (1994). The Chemical Elements. New York: Franklin Watts. ISBN 978-0-531-12501-4.
- Rigden, John S. (2002). Hydrogen: The Essential Element. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-531-12501-4.
- Romm, Joseph J. (2004). ISBN 978-1-55963-703-9.
- Scerri, Eric (2007). The Periodic System, Its Story and Its Significance. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-530573-9.
External links
- Basic Hydrogen Calculations of Quantum Mechanics
- Hydrogen at The Periodic Table of Videos(University of Nottingham)
- High temperature hydrogen phase diagram
- Wavefunction of hydrogen



